life sciences and healthcare News
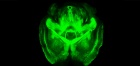
Getting CLARITY: Hydrogel process developed at Stanford creates transparent brain
Wednesday, April 10, 2013
Stanford bioengineers have transformed an intact, post-mortem mouse brain into a transparent three-dimensional structure that keeps all the fine wiring and molecular structures in place. Known as CLARITY, the technique stands to transform our understanding of the brain and indeed of any biological tissue.
President Obama's new $100 million brain research initiative taps several Stanford scientists
Wednesday, April 3, 2013
The Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) project, which calls for initial federal funding of $100 million, will make use of several innovative technologies invented by Stanford scientists.
Biological transistor enables computing within living cells
Wednesday, March 27, 2013
A team of Stanford University bioengineers has taken computing beyond mechanics and electronics into the living realm of biology. They have developed a biological transistor made from genetic material — DNA and RNA. The team calls its invention the “transcriptor.”
A high-resolution endoscope as thin as a human hair
Tuesday, March 12, 2013
Engineers at Stanford have developed a prototype single-fiber endoscope that improves the resolution of these much-sought-after instruments fourfold over existing designs. The advance could lead to an era of needle-thin, minimally invasive endoscopes able to view features out of reach of today’s instruments.
Stanford scientist joins call for major brain research project
Monday, March 11, 2013
Stanford Professor Karl Deisseroth joins a super-team of scientists to propose the Brain Activity map, a collaborative initiative akin to the Human Genome Project, to better understand how the brain works.
Fellowship student Paurakh Rajbhandary advancing medical imaging
Monday, February 4, 2013
Paurakh Rajbhandary, the Brion Founders Graduate Fellow in the School of Engineering, discusses how he is using his fellowship to study medical imaging.
Graduate Fellow Christy Amwake tackles debilitating diseases
Monday, February 4, 2013
Christy Amwake, the Magda Hammam Fellow in the School of Engineering, discusses how her fellowship has freed her to study cures for debilitating diseases.
The 30-year story behind one cancer drug
Monday, January 14, 2013
Vismodegib—also know by its brand name Erivedge—is the first class of drugs that treats inoperable basal cell carcinomas by inhibiting one of the key regulators in human development: the hedgehog molecular signaling pathway. Bioengineer Matthew Scott was a key player in the history of hedgehog gene research.
Stanford researchers develop acrobatic space rovers to explore moons and asteroids
Sunday, December 30, 2012
An autonomous system for exploring the solar system's smaller members, such as moons and asteroids, could bring us closer to a human mission to Mars.
Summer in Shanghai
Thursday, December 13, 2012
Michael Si spent a memorable summer in Shanghai with Stanford's China Internship Program developing new skills and making new friends.
Bioengineers induce, relieve depression symptoms in mice using light
Wednesday, December 12, 2012
Researchers at Stanford have pinpointed well-defined types of neurons within a specific brain region to directly tie them to the control of several symptoms of major depressive illness. Using optogenetics they can turn the symptoms on and off using light. The findings provided a much more detailed understanding of the brain circuitry of depression and could lead to concepts that help people suffering from depression.
Team awarded grant to develop clean drinking water technology
Friday, December 7, 2012
Stanford undergraduate students receive prestigious federal recognition.
Optogenetics illuminates pathways of motivation through brain, study shows
Tuesday, November 20, 2012
Researchers Karl Deisseroth and Melissa Warden led a team that used optogenetics to identify the pathways in our brains that prompt us to act. Their findings could help explain how these pathways become dysfunctional in people suffering from major depression.
A leap forward in brain-controlled computer cursors
Sunday, November 18, 2012
Stanford researchers have designed the fastest, most accurate algorithm yet for brain-implantable prosthetic systems that can help disabled people maneuver computer cursors with their thoughts. The algorithm’s speed, accuracy and natural movement approach those of a real arm, doubling performance of existing algorithms.
Researchers develop light-based 'remote control' for proteins inside cells
Thursday, November 15, 2012
Scientists at Stanford have developed an intracellular remote control: a simple way to activate and track proteins, the busiest of cellular machines, using beams of light.
Bioengineer Prakash wins Gates Foundation global health “Explorations” grant
Thursday, November 1, 2012
The $100,000 award goes to develop and field test an ultra-low-cost paper microscope designed for disease diagnostics.
Stanford researchers measure impact of football concussions
Wednesday, October 24, 2012
Preventing concussions in football requires first knowing what types of hits cause them. Stanford scientists have developed technologies that will help unlock that mystery.
Identification of microbes in healthy lungs sheds light on cystic fibrosis in new study
Thursday, September 27, 2012
New research from the Stanford School of Medicine and of Engineering and the Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital shows that healthy lungs play host to a diverse community of microbes in marked contrast to the bacteria found in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. The findings could have wide implications for treatment of cystic fibrosis and other lung diseases.
Stanford Bioengineers Introduce ‘Bi-Fi’ — The Biological Internet
Tuesday, September 25, 2012
Using an innocuous bacterial virus, bioengineers have created a biological mechanism to send genetic messages from cell to cell. The system greatly increases the complexity and amount of data that can be communicated between cells and could lead to greater control of biological functions within cell communities.
Bioengineer Karl Deisseroth wins NIH Transformative Research Award
Thursday, September 13, 2012
The Transformative Research Award supports exceptionally innovative or unconventional research projects with the potential to change fundamental paradigms.
Bioengineer Christina Smolke wins NIH Director's Pioneer Award
Thursday, September 13, 2012
The award includes a five-year, $2.5 million grant for highly innovative approaches with the potential to affect biomedical or behavioral research. Smolke studies the use of microbes to produce complex chemicals to advance natural-product drugs.
No kick from organic: Little evidence of health benefits, Stanford study finds
Tuesday, September 4, 2012
Researchers from the schools of engineering and medicine studied the health effects of organic foods and found little strong evidence they are more nutritious or carry fewer health risks beyond a reduced the risk of pesticide exposure.
Stanford engineers create a tiny, wirelessly powered cardiac device
Friday, August 31, 2012
Stanford electrical engineers overturn existing models to demonstrate the feasibility of a millimeter-sized, wirelessly powered cardiac device. The findings could dramatically alter the scale of medical devices implanted in the human body.
Stanford biologist and computer scientist discover the 'anternet'
Friday, August 24, 2012
A collaboration between a Stanford ant biologist and a computer scientist has revealed that the behavior of harvester ants as they forage for food mirrors the protocols that control traffic on the Internet.